Aug 9, 2023
2022-2023 Powdery Mildew of Lettuce Fungicide Trial
Bindu Poudel-Ward, Martin Porchas Sr., Martin Porchas Jr., Neeraja Singh, Johan Murcia, and Rebecca Ramirez, and Jason Furr
Yuma Agricultural Center, University of Arizona, Yuma, AZ
This study was conducted at the Yuma Valley Agricultural Center. The soil was a silty clay loam (7-56-37 sand-silt-clay, pH 7.2, O.M. 0.7%). Lettuce was seeded, then sprinkler-irrigated to germinate seed on Nov 15, 2022 on double rows 12 in. apart on beds with 42 in. between bed centers. All other water was supplied by furrow irrigation or rainfall. Treatments were replicated five times in a randomized complete block design. Each replicate plot consisted of 25 ft of bed, which contained two 25 ft rows of lettuce. Plants were thinned Jan 5, 2023 at the 3-4 leaf stage to a 12-inch spacing. Treatment beds were separated by single nontreated beds. Treatments were applied with a tractor-mounted boom sprayer that delivered 50 gal/acre at 100 psi to flat-fan nozzles spaced 12 in apart.
|
Month
|
Max
|
Min
|
Avg
|
Rain
|
|
November (2022)
|
74°F
|
47°F
|
60°F
|
0.00
|
|
December (2022)
|
69°F
|
42°F
|
54°F
|
0.11
|
|
January
|
67°F
|
42°F
|
55°F
|
0.16
|
|
February
|
70°F
|
41°F
|
55°F
|
0.37
|
|
March
|
75°F
|
46°F
|
62°F
|
0.28
|
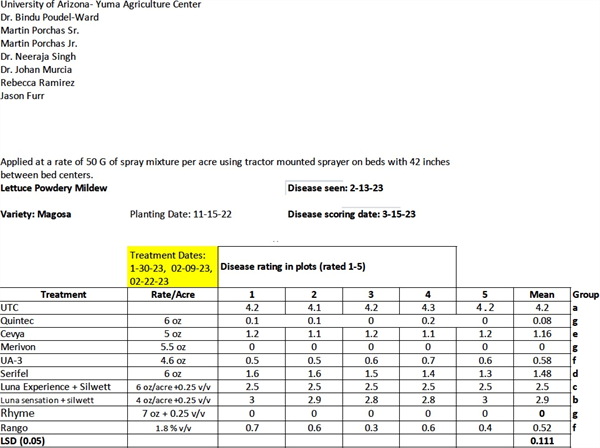
Powdery mildew (caused by Golovinomyces cichoracearum) efficacy trial treatments were made on January30 2023, February 9, 2023 and February 22, 2023.Disease was first seen on February 13,2022. Disease rating was done on March 15, 2022. Disease severity was determined by rating 10 plants within each of the four replicate plots per treatment using the following rating system: 0 = no powdery mildew present; 0.5 = one to a few very small powdery mildew colonies on bottom leaves; 1 = powdery mildew present on bottom leaves of plant; 2 = powdery mildew present on bottom leaves and lower wrapper leaves; 3 = powdery mildew present on bottom leaves and all wrapper leaves; 4 = powdery mildew present on bottom leaves, wrapper leaves, and cap leaf; 5 = powdery mildew present on entire plant. These ratings were transformed to percentage of leaves infected values before being statistically analyzed. Yield loss due to rejected lettuce heads would likely begin to occur on plants with a powdery mildew rating above 2.0 (percentage of leaves infected value of 40).
The data in the table illustrate the degree of disease control obtained by application of the various treatments in this trial. All treatments significantly reduced the final severity of powdery mildew compared to nontreated plants. The most effective fungicides were Rhyme, Merivon and Quintec.
To contact Bindu Poudel go to:
bpoudel@email.arizona.edu











