The Nutrient Budget Tool is a resource for growers who are interested in adequately providing the correct amount of nutrients for their crops for the optimal yields. This tool allows growers to choose crop type and yield goals into a spreadsheet that will then output the needed fertilizer levels of N, P, K needed to meet projected yield goals. Soil test, irrigation water test, and manure nutrient test analysis results can also be input to calculate the overall results of a crop’s nutrient/fertilizer needs. This tool is designed to help promote soil testing and analysis and to help growers be more cost and nutrient efficient. We plan to expand the Nutrient Budget Tool in the future to incorporate soil salinity levels (EC) and pH to better service the nutrient budget users and provide greater information.
Download:
1. Choose the crop from the list of tabs at the bottom of the screen.
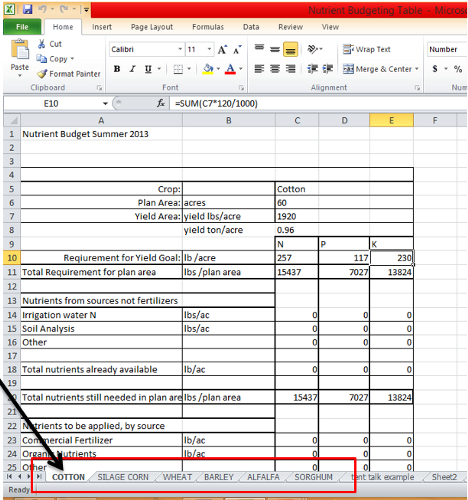
2. Fill in the “Plan Area” field in acres and “Yield Area” field in lbs/acre or tons/acre. Doing this will provide the needed N, P, and K requirements of the specified plan area.
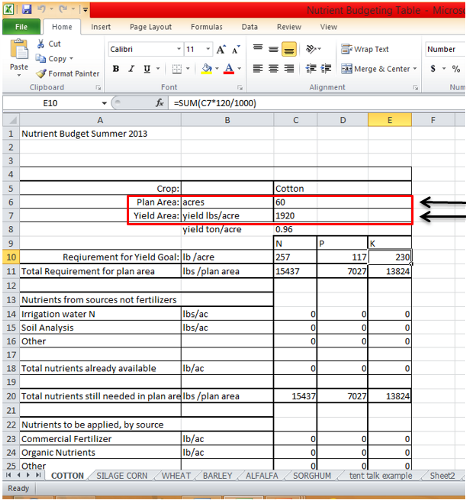
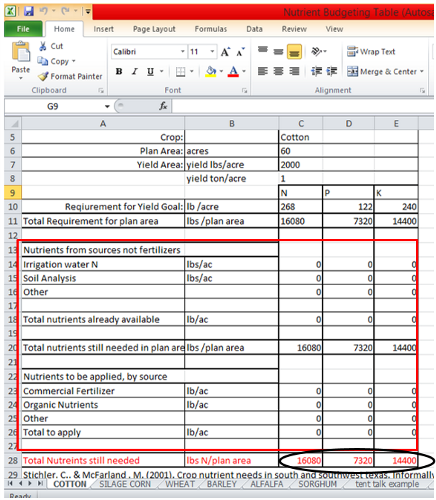
3. Additional numbers from irrigation water analysis, soil analysis and fertilizer analysis from a plan area can be input to factor in to the overall needed requirements for N, P, and K in lbs/plan area.
The other aspect of soil evaluation that is important is that of the chemical condition. Soils are very active chemically and they can differ a great deal in terms of chemical conditions present. The soil chemical environment is very important in that it determines the composition of the soil solution within which the roots live and function, which directly impacts plant nutrition. Physiologically, plant nutrition is clearly recognized as a fundamental aspect of a healthy, vigorous, and productive cotton plant. Accordingly, soil testing has become an integral part of modern agriculture and certainly for cotton production. In developing an assessment of soil chemical conditions or a soil fertility evaluation, it is probably worthwhile to review some basic aspects of making a soil fertility program functional and profitable. This would be true if we were dealing only with problem areas or entire fields.
As an example, soil pH conditions alone (the degree of acidity or basicity that is present) can have a strong impact on nutrient availability, root growth, and over- all plant health. In some portions of the cotton belt (particularly in the Southeast), acid subsoils can reduce or prevent root growth, which can limit the depth of the soil profile utilized by the plant and have a similar end result as the gravel layer. This condition may not be detected by augering through the soil and visually inspecting it, but it would be readily apparent if soil samples were collected at regular depth intervals and subjected to a simple pH analysis.