-
Nov 27, 2024Weather Impacts Insect Abundance and Activity
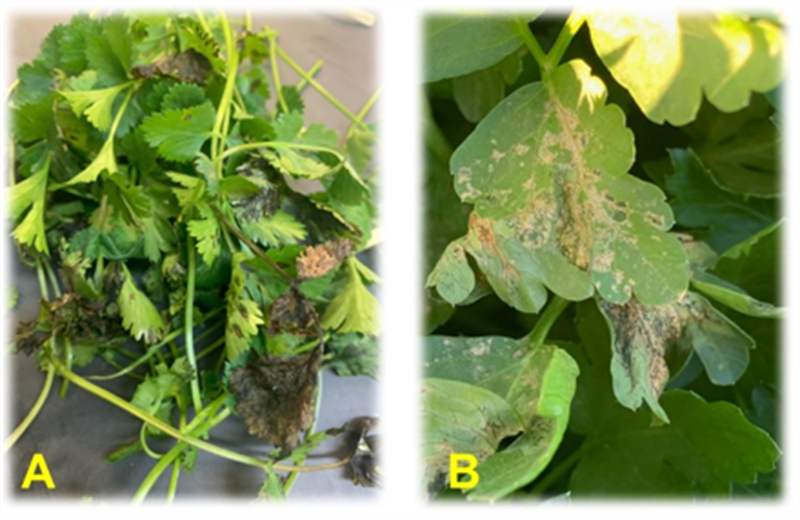
We all know that weather influences produce crop growth and ultimately can create wide fluctuations in markets. Similarly, our local weather can significantly impact pest activity and abundance on desert produce crops. You have probably noticed a decline in insect activity over the past 2 weeks. These changes are consistent with cooler, seasonal temperatures. For insects, their activity and abundance are closely aligned with weather. The reason for this is that temperature is the driving force behind insect development, growth and behavior. Unlike many animals, insects are poikilothermic (“cold-blooded”); that is, they are unable to regulate their body temperature. Their internal temperature varies along with that of the ambient environmental temperature. Consequently, insect pests such as whiteflies, beet armyworms, cabbage loopers, diamondback moths, and leaf miners are most active and develop rapidly when temperatures average ~86° F; in contrast, they are less active and develop much slower under cool, winter conditions. That is one of the primary reasons these insect pests can be so abundant on produce crops in Sep-Nov. Behavioral activities such as flight, movement, reproduction, feeding and oviposition are similarly influenced by seasonal temperatures. But temperature requirements for insects vary with species (see table below). For example, the optimal temperature for growth and development of beet armyworms and diamondback moths is the same (86 °F), but diamondback moth can complete a generation quicker and can develop over a much broader range of temperature. Thus, they can be more problematic season long if not adequately controlled. Then you have Bagrada bug which tend to prefer warmer weather for development. Its lower developmental threshold of 62°F is the main reason the pest is generally hard to find during the winter months. In contrast, green peach aphids, which we annually find on winter produce crops, thrive in cooler weather (optimal temperature for growth is 55°F. That’s the main reason we don’t find them on summer crops; it is just too hot for them. In general, extreme hot (> 120°F) or cold temperatures (<32 °F), can be lethal or greatly restrict insect growth and behavior. Consequently, temperature and other weather factors such as rainfall, humidity, sunlight and wind play a major role in determining insect activity and abundance on local desert crops. For a more detailed explanation on the impact of weather on insects go to my publication: Weather Influences Insect Pest Abundance.
 To contact John Palumbo go to: jpalumbo@ag.Arizona.edu
To contact John Palumbo go to: jpalumbo@ag.Arizona.edu