
Everything we eat and much of what we are surrounded by in our daily lives have a common base from water and the production of green plants. Anything made of carbon, even if the immediate source of carbon is a petroleum-based product, has an original derivation that starts with green plants and water.
Green plants perform the miraculous process of photosynthesis that captures light energy from the sun to combine with water (H2O) taken up from the soil through the root system, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, forming a simple 6-carbon carbohydrate compound (C6H12O6), and liberating free oxygen (O2) into the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis involves a complex system of biochemical reactions, but the fundamental photosynthesis process can be reduced to very simple terms as outlined in Figure 1.
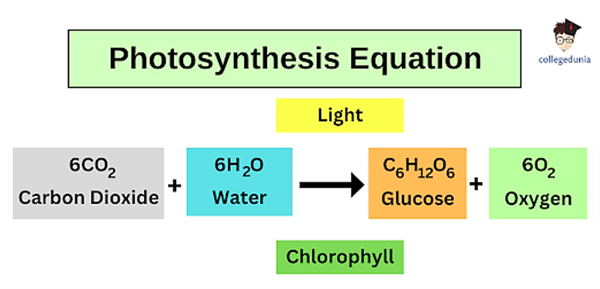
Figure 1. Basic photosynthesis reaction. (Source: Collegedunia).
Figure 2 offers a little more detail in the photosynthetic process and there is still more to the story. But the essentials are outlined in Figures 1 and 2.
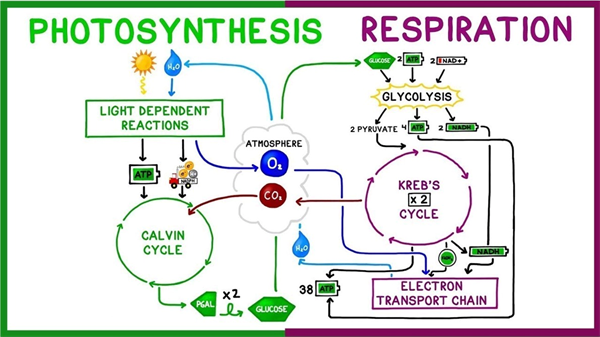
Figure 2. Connections between photosynthesis and plant respiration.
The process of taking CO2 from the atmosphere and “fixing” the carbon in a larger and more complex form as a basic carbohydrate (simple sugar compound) is referred to as “carbon fixation” and green plants provide most of this primary function in the earth terrestrial, or land-based ecosystems.
Carbon fixation is conducted by organisms containing chlorophyll and green plants do most of this work. There are also some species of algae and cyanobacteria that can fix carbon from the atmosphere. But green plants, using energy from the water and water from the soil are the real workers in our world in this regard.
Water is essential in this process of fixing carbon through photosynthesis. In fact, six units of water are required for every unit of carbohydrate that is produced (Figure 1).
Additional water is used by the plant in the transpiration process, which is the movement of water from the soil through the root system, through the conductive tissues of the plant. This provides for good cellular hydration and biological function. In the transpiration process water moves out of the plant and escapes into the atmosphere as gas through the stomates, which are small openings in the underside of plant leaves (Figure 3).
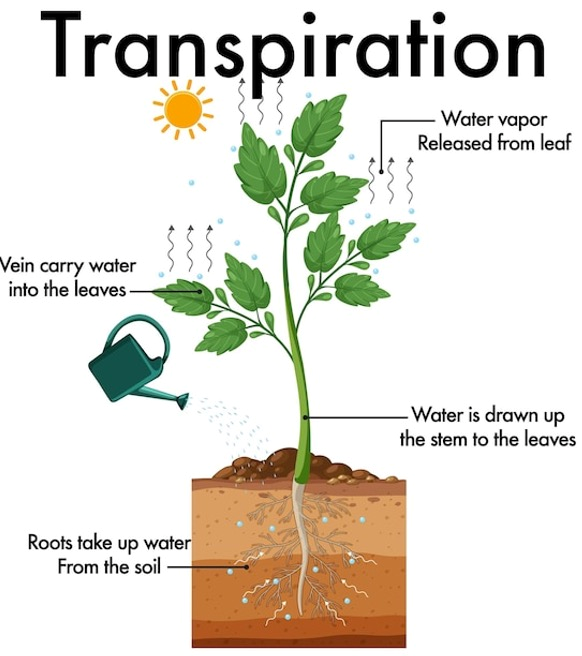
Figure 3. Plant transpiration. Source: Premium Vector
Through this process of photosynthesis, water and green plants serve as the backbone of all terrestrial life. These are fundamental facts and critical functions that we manage in crop production systems. Essentially, every field with a green crop growing is a photosynthetic factory and water is always an essential component.
Consumers directly benefit from the water used to produce the crops with all the fruits and vegetables that come from them. Healthy animals require good food, which all comes from plants, i.e., alfalfa. Everything we consume has a significant water footprint and much of that involves supporting plant photosynthesis.
The inescapable fact is that we need the plants, and the plants need water to grow and produce.
Frost and freeze damage affect countless fruit and vegetable growers leading to yield losses and occasionally the loss of the entire crop. Frost damage occurs when the temperature briefly dips below freezing (32°F).With a frost, the water within plant tissue may or may not actually freeze, depending on other conditions. A frost becomes a freeze event when ice forms within and between the cell walls of plant tissue. When this occurs, water expands and can burst cell walls. Symptoms of frost damage on vegetables include brown or blackening of plant tissues, dropping of leaves and flowers, translucent limp leaves, and cracking of the fruit. Symptoms are usually vegetable specific and vary depending on the hardiness of the crop and lowest temperature reached. A lot of times frost injury is followed by secondary infection by bacteria or opportunist fungi confusing with plant disease.
Most susceptible to frost and freezing injury: Asparagus, snap beans, Cucumbers, eggplant, lemons, lettuce, limes, okra, peppers, sweet potato
Moderately susceptible to frost and freezing injury: Broccoli, Carrots, Cauliflower, Celery, Grapefruit, Grapes, Oranges, Parsley, Radish, Spinach, Squash
Least susceptible to frost and freezing injury: Brussels sprouts, Cabbage, Dates, Kale, Kohlrabi, Parsnips, Turnips, Beets
More information:
Interested in staying up to date on the latest robotic ag technologies? The International Forum for Agricultural Robotics, FIRA, hosts two annual conferences focusing on robotics and autonomous farming solutions, one in Europe and one in the USA. They recently uploaded recordings of sessions from the 2024 World FIRA, held in Toulouse, France to YouTube. The site also contains playlists of themed breakout sessions from previous European and USA events (over 400 videos total). Highlights include panel discussions with growers and company executives, robot demos, and inno’pitches from startup companies. Most of the content, particularly from the USA events, is high quality and worth viewing.
Check it out by clicking here or on the image below.
The following is the FIRST WEED SCIENCE ARTICLE OF THIS NEWSLETTER published January 13, 2010 by our friend Barry Tickes.
The selective grass herbicides are good rescue type treatments in vegetables for grasses that have gotten through Pefar, Kerb and Balan. These include Poast (sethoxydim), Select (clethodim) and Fusilade (fluazifop) and the generics of these products. These herbicides are all slow and even slower as temperature and day length drop. If you don't like weeds, you can have the satisfaction of watching them suffer for a long time. Treated grasses should stop growing immediately and will slowly turn yellow, red and gradually disappear as the crop grows. This will likely take 2 to 3 weeks. Poast is the slowest and Select is the fastest. All of these herbicides require the addition of a crop oil concentrate except for Select Max which you can use with either a crop oil concentrate or non-ionic surfactant. Some reports indicate that ammonium sulfate will help in cold weather. If you have used one of these products and don't see adequate control within 3 or 4 weeks, please contact us and we'll look at it with you.
As Barry promised in his 2010 article he will be looking at some field trials with me today!

Results of pheromone and sticky trap catches can be viewed here.
Corn earworm: CEW moth counts remain at low levels in all areas, well below average for this time of year.
Beet armyworm: Trap increased areawide; above average compared to previous years.
Cabbage looper: Cabbage looper counts decreased in all areas; below average for this time of season.
Diamondback moth: DBM moth counts decreased in most areas. About average for this time of the year.
Whitefly: Adult movement beginning at low levels, average for early spring.
Thrips: Thrips adult counts reached their peak for the season. Above average compared with previous years.
Aphids: Aphid movement decreased in all areas; below average for late-March.
Leafminers: Adults remain low in most locations, below average for March.