Soils with excess soluble salts, saline soils, and/or excess sodium (Na+) concentrations (sodic) are a natural feature of desert soils and common in arid land agriculture. This is primarily due to an accumulation of soluble salts near the soil surface as water evaporates from the soil surface.
Saline soils are a problem in crop production systems because of the sensitivity to salinity of crop plants, although plants vary in their degree of sensitivity. The period of greatest plant sensitivity to salinity is in the early stages of development, during germination and stand establishment.
Sodic soils are a problem in crop production systems because of the adverse effects of excess sodium on soil structure, causing a dispersion of soil particles and the breakdown of soil aggregates. This leads to poor water infiltration and percolation in the soil profile.
Some basic points associated with saline and/or sodic soils and management are outlined in the following sections.
https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/PA_NRCSConsumption/download/?cid=nrcseprd589210&ext=pdf
Sodic soil reclamation does require an amendment that will facilitate the chemical exchange of Na+, usually from a calcium (Ca2+) source, such as gypsum (CaSO4).
An effective and straightforward method of calculating a leaching requirement (LR) can be calculated with the following equation that was presented by the USDA Salinity Laboratory (Ayers and Westcot, 1989).
Leaching Requirement (LR) Calculation:
Where:
ECw = salinity of the irrigation water, electrical conductivity (dS/m)
ECe = critical plant salinity tolerance, electrical conductivity (dS/m)
i.Drip irrigation systems are commonly very limited in this respect.
i.Examples: wheat, alfalfa, sudangrass, etc.
I am seeking samples of downy mildew on lettuce from around Yuma County to support the Michelmore Lab and their ongoing efforts to help characterize the downy mildew populations of the United States. The Michelmore Lab has led the charge on a survey of Bremia variants since 1980 and has been instrumental in demystifying the gene-for-gene nature of lettuce resistance to downy mildew.
Their group invites growers across the United States to submit downy mildew infected plant samples, which are then used to culture the Bremia on live host plants. The team then inoculates a panel of lettuce varieties carrying known resistance genes to determine the race of each isolate they receive. Identifying which races occur in which specific fields is essential to guiding the breeding of new resistant cultivars and maximizing the effectiveness of host-based genetic disease management. The data obtained from these tests are also used to designate new Bremia races through the International Bremia Evaluation Board.
Your contribution will help breed better lettuce for Yuma. This means less breakdown of resistance in the field, and better yields for Yuma growers. To facilitate these submissions the Yuma Plant Health Clinic will be setting up a separate drop-off point and submission sheet for downy mildew sample submissions in the same hallway we use for standard plant diagnostic submissions. The drop-off point will be clearly labelled and consist of a chest-style refrigerator and printed copies of the submission form. It is vital to keep these samples cool so they remain viable for future inoculations, so please place your samples inside of the refrigerator before you leave.
Shipping will be handled by the clinic. All we ask is that you fill out the submission form as completely as you can. An example of the questions that are asked in that form so you can prepare ahead of time can be found HERE .Interested in staying up to date on the latest robotic ag technologies? The International Forum for Agricultural Robotics, FIRA, hosts two annual conferences focusing on robotics and autonomous farming solutions, one in Europe and one in the USA. They recently uploaded recordings of sessions from the 2024 World FIRA, held in Toulouse, France to YouTube. The site also contains playlists of themed breakout sessions from previous European and USA events (over 400 videos total). Highlights include panel discussions with growers and company executives, robot demos, and inno’pitches from startup companies. Most of the content, particularly from the USA events, is high quality and worth viewing.
Check it out by clicking here or on the image below.
There are many different types of pests that affect crops grown in Arizona. The three types of pests most often cited as the source of most problems are insects, diseases and weeds. These are the same types of pests that are cited as causing the major agricultural pest problems across the U.S. and worldwide. Graphs 1-3 illustrate, however, that the relative importance of these types of pest problems differ in Arizona from the rest of the U.S. and worldwide. In terms of pesticide use, worldwide herbicides accounted for 36% of total usage, insecticides 25%, and fungicides 10% and other 29% (nematicides, rodenticides, fumigants, bird, fish and aquatic pests). In the U.S., herbicides accounted for 44%, insecticides 10%, fungicides 6%, and other 40% of pesticide use. In Arizona, however, insecticides accounted for 58%, herbicides 17% and fungicides 12%. This is only an indirect measure of the relative importance of these three areas of pest management and may be heavily influenced by the amount of pesticides used. For instance, it is common to spray for insects five or more times per season while it is uncommon to spray for weeds more than twice. None the less, these graphs illustrate that weeds are the predominant pest problem in agricultural areas across the U.S. and worldwide.

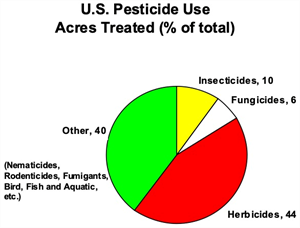

We wanted to share the information above obtained from the PCA Study Guide Section VI prepared by our "amigo" Barry Tickes who is teaching the Applied Weed Science Class at the University of Arizona this semester.
